Understanding Cloud Governance and Compliance Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on cloud governance and compliance architecture. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of managing and securing data in the cloud, ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks, and implementing robust governance practices. Whether you are an IT professional, a business owner, or simply curious about the evolving landscape of cloud technology, this article will provide you with valuable insights and actionable knowledge.
Introduction to Cloud Governance
Cloud governance is a set of policies, processes, and controls that organizations put in place to ensure the effective and secure management of cloud resources. It encompasses various aspects such as data security, compliance, cost optimization, and risk management. By establishing a comprehensive cloud governance framework, organizations can maximize the benefits of cloud technology while minimizing risks and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Why is Cloud Governance Important?
Effective cloud governance is crucial for organizations for several reasons:
1. Cost Optimization: Cloud governance helps organizations optimize cloud costs by effectively managing resource allocation, monitoring usage, and implementing cost-saving strategies such as rightsizing instances and leveraging reserved instances.
2. Risk Management: Cloud governance enables organizations to identify and mitigate risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and service disruptions. It helps establish robust security controls, disaster recovery plans, and incident response procedures.
3. Compliance with Regulatory Frameworks: Cloud governance ensures organizations adhere to relevant regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. It helps implement appropriate security controls, data privacy measures, and audit trails to demonstrate compliance.
4. Operational Efficiency: By establishing standardized processes and procedures, cloud governance enhances operational efficiency. It streamlines resource provisioning, automates routine tasks, and promotes collaboration between IT teams and business stakeholders.
In the following sections, we will explore various aspects of cloud governance and compliance architecture in detail.
Compliance in the Cloud
Ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks is a critical aspect of cloud governance. Organizations must adhere to industry-specific regulations and standards to protect sensitive data and maintain customer trust. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties and reputational damage. Let’s explore some key considerations related to compliance in the cloud.
Understanding Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) impose specific requirements on organizations handling personal data or protected health information. Understanding the scope and implications of these regulations is essential for designing and implementing a compliant cloud architecture.
Organizations must conduct a thorough assessment of their data and identify the applicable regulatory requirements. They must ensure that their cloud service providers also comply with these regulations and have appropriate security controls and certifications in place.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are paramount in the cloud. Organizations must implement robust measures to protect customer data and prevent unauthorized access. Encryption, both in transit and at rest, should be employed to safeguard sensitive information.
Access controls should be established to ensure that only authorized personnel can access data. Multi-factor authentication, role-based access control (RBAC), and strong password policies are some of the measures that can be implemented to enhance data security.
Data Residency and Sovereignty
Many jurisdictions have strict regulations governing the storage and processing of data within their borders. Organizations must consider data residency requirements to ensure compliance. Cloud service providers should be chosen based on their ability to meet these requirements.
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it is located. Organizations must understand the implications of data sovereignty and ensure that their cloud providers adhere to the applicable laws.
Audit Trails and Compliance Reporting
Establishing audit trails is crucial for demonstrating compliance and ensuring accountability. Organizations should implement logging and monitoring mechanisms to track user activities, system events, and access attempts. These logs should be stored securely and regularly reviewed to detect and investigate any suspicious activities.
Compliance reporting involves providing evidence of adherence to regulatory requirements. Organizations should maintain proper documentation and implement processes to generate compliance reports as needed. These reports can be requested during audits or investigations.
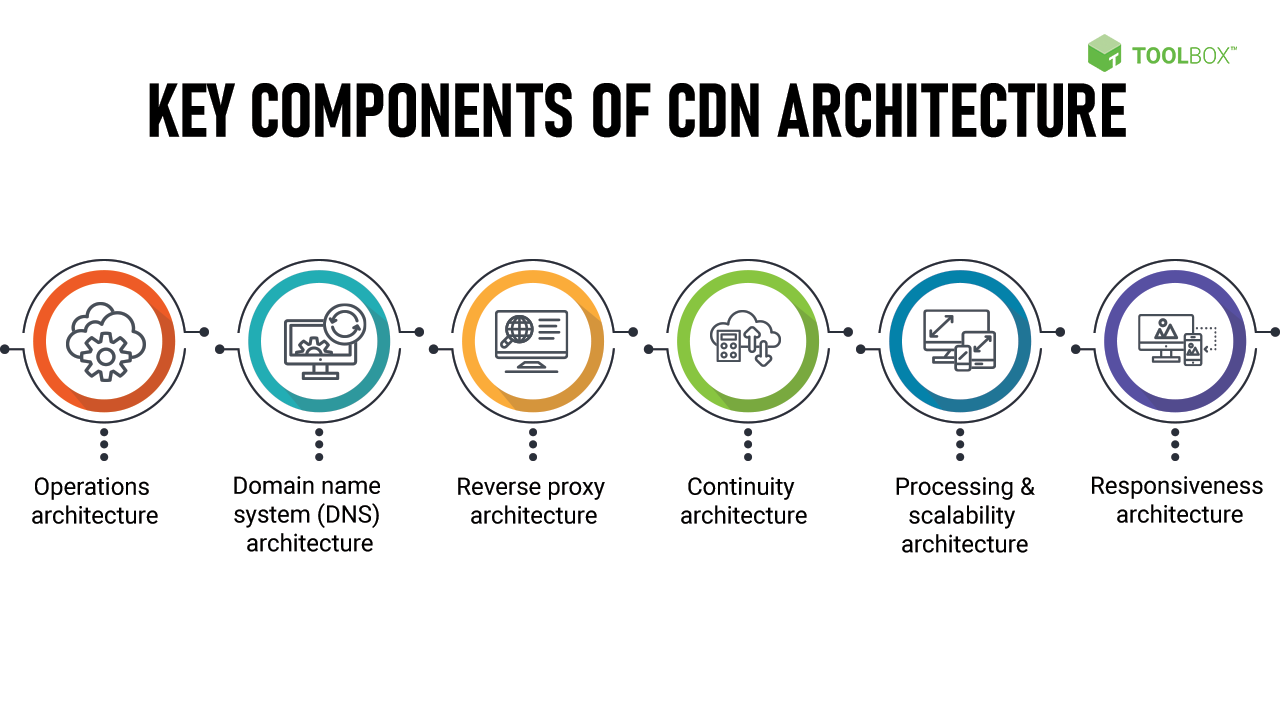
Building Blocks of Cloud Compliance Architecture
A robust cloud compliance architecture comprises various building blocks that work together to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and industry best practices. Let’s explore these building blocks in detail.
Risk Assessments
Performing regular risk assessments is a fundamental step in building a compliant cloud architecture. Organizations must identify and evaluate potential risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and service disruptions. This assessment helps prioritize security controls and allocate resources effectively.
Risk assessment methodologies such as threat modeling, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing can be employed to identify vulnerabilities and assess the impact of potential security incidents.
Security Controls
Implementing robust security controls is essential to protect data and maintain compliance. Various security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data loss prevention (DLP) solutions can be deployed to safeguard cloud resources.
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting data in transit and at rest. Organizations should utilize encryption mechanisms to ensure that sensitive information remains secure even in the event of unauthorized access.
Identity and Access Management
Identity and access management (IAM) is crucial for maintaining compliance in the cloud. Organizations must establish strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to prevent unauthorized access to cloud resources.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is an effective approach to managing user access permissions. It ensures that users have access only to the resources and data necessary to perform their job functions.
Change Management
Change management processes are essential to maintain the integrity and compliance of the cloud environment. Organizations should implement policies and procedures to govern changes to cloud resources, configurations, and applications.
Change management processes should include thorough testing, documentation, and approval mechanisms to ensure that changes are implemented in a controlled and compliant manner.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuous monitoring of cloud environments is critical for detecting and responding to security incidents promptly. Organizations should implement monitoring tools and establish processes to review logs, track system events, and generate alerts.
Incident response plans should be developed to outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. These plans should include procedures for containment, investigation, and recovery, as well as mechanisms for reporting incidents to relevant stakeholders.
Vendor Management and Due Diligence
Cloud service providers (CSPs) play a significant role in maintaining compliance. Organizations must conduct due diligence when selecting a CSP to ensure that they meet the necessary security and compliance requirements.
Vendor management processes should be established to monitor the performance of CSPs, regularly assess their compliance posture, and ensure that contractual agreements align with regulatory requirements.
Data Governance in the Cloud
Data governance encompasses the processes, policies, and controls that organizations put in place to manage and protect their data. In the context of cloud governance and compliance, data governance plays a crucial role in ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. Let’s explore the key aspects of data governance in the cloud.
Data Classification
Data classification involves categorizing data based on its sensitivity and criticality. Organizations should implement a data classification framework that aligns with regulatory requirements and business needs.
By classifying data, organizations can apply appropriate security controls and define access policies based on the level of sensitivity. This helps ensure that data is adequately protected and accessed only by authorized personnel.
Data Access Controls
Implementing robust access controls is essential to protect data in the cloud. Organizations should enforce the principle of least privilege, granting users access only to the data and resources necessary to perform their job functions.
Access controls can be implemented at various levels, including infrastructure, application, and data. Role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), and fine-grained access control mechanisms can be employed to ensure appropriate access rights.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a critical component of data governance in the cloud. Organizations should employ encryption mechanisms to protect data both in transit and at rest.
Transport Layer Security (TLS) can be used to encrypt data in transit between clients and cloud services. Additionally, data at rest should be encrypted using robust encryption algorithms. Encryption keys should be securely managed to prevent unauthorized access.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions help organizations detect and prevent the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data. These solutions use techniques such as content inspection, contextual analysis, and data fingerprinting to identify and mitigate risks associated with data leakage.
Organizations should implement DLP solutions in their cloud environments to ensure compliance with data protection regulations and prevent data breaches.
Data Retention and Deletion
Organizations must establish policies and procedures for data retention and deletion to comply with regulatory requirements. Data should be retained for the required duration and securely deleted when no longer needed.
Effective data lifecycle management ensures that data is retained only as long as necessary and disposed of in a manner that prevents unauthorized access.
Identity and Access Management
Identity and access management
(continued) Identity and Access Management
Identity Lifecycle Management
Identity lifecycle management involves the processes and controls for managing user identities throughout their lifecycle within an organization. This includes activities such as user provisioning, deprovisioning, role management, and access request and approval.
Organizations should have well-defined processes and tools in place to ensure that user identities are created, modified, and deactivated according to established policies and procedures. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that users have the appropriate level of access rights based on their roles and responsibilities.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing cloud resources. This typically involves a combination of something the user knows (password), something the user has (smart card or mobile device), and something the user is (biometric data).
Implementing MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, as even if an attacker obtains a user’s password, they would still need the additional factors to gain access. Organizations should consider implementing MFA for all critical cloud resources and privileged accounts.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged access management (PAM) focuses on securing and monitoring privileged accounts and their access to sensitive resources. Privileged accounts, such as administrator accounts, have elevated privileges and control over critical systems and data.
PAM solutions help organizations control and monitor privileged access by enforcing strict authentication, authorization, and auditing mechanisms. They also provide session monitoring and recording capabilities to detect and investigate any suspicious activities performed by privileged users.
Access Reviews and Recertification
Regular access reviews and recertification processes are essential to ensure that user access rights remain appropriate and aligned with business needs. Access reviews involve reviewing and validating user access permissions to ensure that they are still valid and necessary.
Organizations should establish a periodic review process, which may include managers or data owners reviewing and confirming the access rights of their team members. This helps prevent unauthorized access and ensures that access privileges are aligned with the principle of least privilege.
Cloud Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Securing the cloud environment requires continuous monitoring and prompt incident response. Organizations must implement robust security monitoring mechanisms and establish effective incident response procedures to detect, respond to, and mitigate security incidents. Let’s explore these aspects in more detail.
Log Management and Monitoring
Log management and monitoring involve the collection, storage, and analysis of logs from various cloud resources and systems. Organizations should implement centralized log management solutions and configure logging for all critical resources.
Monitoring logs helps detect anomalous activities, unauthorized access attempts, and potential security breaches. Automated log analysis tools can be employed to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious activities.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) play a vital role in detecting and mitigating security threats in real-time. These systems monitor network traffic and system activities to identify known attack patterns and suspicious behavior.
Organizations should deploy IDPS solutions in their cloud environments and configure them to alert administrators or trigger automated responses when potential security incidents are detected.
Security Incident Response
Having a well-defined security incident response plan is critical for effectively managing and mitigating security incidents. The plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including containment, investigation, and recovery.
Organizations should establish incident response teams and assign clear roles and responsibilities to team members. Regular testing and simulations of incident response plans help ensure preparedness and identify areas for improvement.
Threat Intelligence and Vulnerability Management
Staying informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities is essential for effective cloud security monitoring. Organizations should subscribe to threat intelligence feeds and regularly update their vulnerability management programs.
Vulnerability scanning and patch management processes should be implemented to identify and remediate vulnerabilities in a timely manner. Continuous monitoring of threat intelligence sources helps identify emerging threats and proactively mitigate risks.
Cloud Service Provider (CSP) Monitoring
Monitoring the security practices and performance of cloud service providers (CSPs) is crucial for maintaining a secure cloud environment. Organizations should regularly review the security controls and compliance posture of their CSPs to ensure they meet the necessary standards.
Contractual agreements with CSPs should include provisions for regular security assessments, audits, and reporting. Organizations should have mechanisms in place to monitor the performance of CSPs and promptly address any security concerns or breaches.
Cloud Governance Frameworks and Standards
Various cloud governance frameworks and standards provide guidance and best practices for organizations to establish effective governance and compliance programs. These frameworks help organizations align their cloud governance efforts with industry-recognized standards. Let’s explore some popular frameworks and standards.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework provides a risk-based approach to managing cybersecurity. It offers a set of core functions, categories, and subcategories that help organizations assess and improve their cybersecurity posture.
The framework focuses on identifying, protecting, detecting, responding to, and recovering from cybersecurity threats. Organizations can use the NIST Cybersecurity Framework as a foundation for their cloud governance and compliance programs.
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an international standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information, including data in the cloud.
Organizations can achieve ISO 27001 certification by implementing a comprehensive set of security controls and demonstrating adherence to the standard’s requirements. ISO 27001 provides a framework for organizations to establish and maintain effective cloud governance and compliance architecture.
CIS Controls
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls is a set of best practices for securing organizations’ IT systems and data. The controls provide a prioritized list of actions that organizations can take to protect against common cyber threats.
The CIS Controls cover a wide range of security areas, including inventory and control of hardware and software assets, continuous vulnerability management, secure configuration for hardware and software, and controlled use of administrative privileges. Implementing the CIS Controls helps organizations establish a solid foundation for their cloud governance and compliance efforts.
Cloud Governance and DevOps
Cloud governance and DevOps are often seen as complementary practices, as both focus on achieving agility and efficiency in the cloud environment. Let’s explore how organizations can integrate cloud governance and DevOps practices effectively.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration and communication between governance teams and DevOps teams are crucial for successful integration. Governance teams should work closely with DevOps teams to understand their requirements, challenges, and priorities.
Regular meetings, joint planning sessions, and shared documentation help align governance and DevOps efforts. Collaboration tools and platforms can facilitate communication and knowledge sharing between the teams.
Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration play a significant role in streamlining governance processes and ensuring compliance in DevOps environments. Organizations should leverage automation tools and platforms to automate governance tasks, such as policy enforcement, provisioning, and compliance monitoring.
Orchestration frameworks can be used to coordinate and integrate various components of the cloud environment, including security controls, monitoring systems, and compliance management tools.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
CI/CD practices enable organizations to deliver software changes rapidly and reliably. By integrating governance checks and compliance validation into the CI/CD pipelines, organizations can ensure that changes adhere to established policies and regulatory requirements.
Automated testing, code analysis, and security scanning can be incorporated into the CI/CD pipelines to detect vulnerabilities and compliance violations early in the development cycle.
Monitoring and Auditing
Monitoring and auditing are essential components of cloud governance in a DevOps environment. Organizations should implement monitoring tools and establish processes to track and analyze DevOps activities, infrastructure changes, and application deployments.
Auditing mechanisms can help ensure that changes are documented, approved, and reviewed for compliance. Regular audits of DevOps processes and environments help identify any gaps or non-compliance issues that need to be addressed.
Cloud Governance Tools and Technologies
A wide array of tools and technologies are available to support organizations’ cloud governance and compliance efforts. These tools help automate governance processes, enforce policies, and provide visibility into cloud resources. Let’s explore some popular cloud governance tools and technologies.
Cloud Management Platforms (CMPs)
Cloud management platforms (CMPs) provide a centralized interface to manage and monitor cloud resources across multiple cloud service providers. CMPs help organizations optimize resource utilization, automate provisioning, and enforce governance policies.
These platforms often include features such as cost management, performance monitoring, policy enforcement, and self-service portals. CMPs streamline governance processes and provide organizations with a holistic view of their cloud environment.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
Security information and event management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze security event logs from various sources, including cloud resources. SIEM systems help organizations detect and respond to security incidents by correlating and analyzingthe collected data. They provide real-time alerts, incident investigation capabilities, and reporting functionalities.
SIEM systems can be integrated with cloud environments to monitor logs from various cloud services, identify potential security threats, and facilitate incident response. They play a crucial role in maintaining the security and compliance of the cloud environment.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools
Data loss prevention (DLP) tools help organizations identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data in the cloud. These tools use content inspection, contextual analysis, and data fingerprinting techniques to detect and prevent unauthorized transmission of sensitive information.
DLP tools can be configured to scan files stored in cloud storage services, monitor network traffic for data exfiltration attempts, and enforce data protection policies. They help organizations maintain data privacy, prevent data breaches, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Configuration Management Tools
Configuration management tools automate the process of managing and tracking changes to cloud resources and configurations. These tools enable organizations to enforce standardized configurations, track configuration drift, and ensure compliance with governance policies.
Configuration management tools provide features such as infrastructure as code (IaC), version control, and automated deployment. They help organizations achieve consistency, scalability, and traceability in their cloud environments, while ensuring compliance with governance requirements.
Compliance Management Platforms
Compliance management platforms help organizations streamline and automate their compliance processes. These platforms provide a centralized repository for storing compliance-related documentation, policies, and procedures.
Compliance management platforms often include features such as policy management, control testing, compliance reporting, and audit management. They help organizations demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements, track compliance status, and streamline the audit process.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) Tools
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools help organizations assess and monitor the security posture of their cloud environments. These tools scan cloud resources, configurations, and network settings to identify security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
CSPM tools provide organizations with visibility into their cloud security posture, highlight areas of non-compliance, and offer recommendations for remediation. They help organizations proactively address security risks and maintain compliance in the dynamic cloud environment.
Future Trends and Challenges in Cloud Governance
The landscape of cloud governance and compliance architecture is constantly evolving, driven by emerging technologies, regulatory changes, and evolving cyber threats. Let’s explore some anticipated future trends and challenges in this field.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies have the potential to transform cloud governance and compliance. These technologies can automate governance processes, enhance security monitoring, and improve threat detection capabilities.
AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies that may indicate security breaches or compliance violations. They can also assist in automating compliance assessments, risk analysis, and incident response.
Cloud-Native Governance
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-native architectures and technologies, cloud-native governance approaches are emerging. Cloud-native governance focuses on leveraging cloud-native tools and platforms to enforce policies, secure resources, and ensure compliance.
Cloud-native governance enables organizations to take advantage of the scalability, agility, and automation capabilities offered by cloud-native technologies. It involves integrating governance controls and processes into the DevOps pipelines and leveraging cloud-native security services.
Data Privacy and International Regulations
Data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, continue to evolve, and new regulations are being introduced in various jurisdictions. Organizations must stay abreast of these regulations and ensure compliance to protect customer data and avoid penalties.
International data transfers and data sovereignty present challenges for cloud governance and compliance. Organizations must navigate the complexities of data residency requirements and ensure that data is stored and processed in compliance with applicable regulations.
Cloud Supply Chain Security
As organizations rely on cloud service providers and engage in multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environments, cloud supply chain security becomes a critical consideration. Organizations must assess the security controls and compliance posture of their CSPs, as well as their third-party vendors and suppliers.
Supply chain attacks and vulnerabilities in the cloud ecosystem can pose significant risks to organizations’ data and operations. Ensuring the security and compliance of the entire cloud supply chain requires robust vendor management practices, regular audits, and thorough due diligence.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is an approach that assumes no trust by default and requires verification for every access request. ZTA focuses on authentication, authorization, and continuous monitoring to ensure the security and compliance of cloud resources.
Implementing a Zero Trust approach involves granular access controls, strong authentication mechanisms, and continuous monitoring of user behavior and network traffic. It helps organizations protect against unauthorized access, insider threats, and lateral movement within the cloud environment.
Skills and Expertise Gap
Ensuring effective cloud governance and compliance requires specialized skills and expertise. However, there is a growing skills gap in this field, as the demand for cloud governance professionals outpaces the availability of qualified individuals.
Organizations must invest in training and upskilling their teams to address this skills gap. They can also engage with third-party experts and consultants to complement their internal capabilities and ensure the success of their cloud governance and compliance initiatives.
In conclusion, cloud governance and compliance architecture are essential components of successful cloud adoption. By implementing robust governance frameworks, organizations can ensure data security, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency in the cloud. The future of cloud governance will be shaped by emerging technologies, evolving regulations, and the need to address new challenges. Staying informed and proactive is key to maintaining a secure and compliant cloud environment.