Cloud Backup and Restore Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on cloud backup and restore architecture! In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of cloud backup and restore architecture, exploring its importance, key components, and best practices. Whether you’re a business owner looking to safeguard your valuable data or an IT professional seeking to enhance your organization’s backup and restore capabilities, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need.
Understanding Cloud Backup and Restore
In today’s digital landscape, where data is a critical asset for businesses, having a robust backup and restore architecture is essential. Cloud backup and restore refers to the process of storing data in remote servers, known as the cloud, and recovering it in the event of data loss or system failure. Unlike traditional backup methods that rely on physical storage devices, cloud backup offers numerous advantages, such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access.
The Advantages of Cloud Backup
One of the key advantages of cloud backup is its scalability. With cloud-based solutions, businesses can easily expand their storage capacity as their data grows, without the need for additional hardware investments. This scalability ensures that organizations can accommodate their evolving backup needs and effectively manage the increasing volumes of data generated.
Another significant advantage is the cost-effectiveness of cloud backup. Traditional backup methods often require businesses to invest in expensive hardware, such as external hard drives or tape drives, and incur maintenance costs. In contrast, cloud backup eliminates the need for such hardware investments and allows businesses to pay for the storage they actually use, making it a more cost-efficient solution.
Additionally, cloud backup offers enhanced accessibility. With data stored in the cloud, businesses can easily access their backups from any location with an internet connection. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in situations where employees need to retrieve data while working remotely or during disaster recovery scenarios when on-site access is not possible.
Key Considerations for Implementing Cloud Backup
While cloud backup offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider certain factors when implementing a cloud backup and restore architecture. Firstly, organizations should evaluate their data storage requirements and choose a cloud backup provider that can meet their specific needs. Factors such as storage capacity, data retention policies, and data transfer speeds should be carefully assessed.
Another crucial consideration is data security. When entrusting sensitive data to a cloud provider, organizations must ensure that appropriate security measures are in place. This includes data encryption both during transmission and at rest, strong access controls, and regular security audits. Choosing a cloud provider with robust security certifications, such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2, can provide additional peace of mind.
Lastly, organizations should consider the recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) when designing their cloud backup architecture. RTO refers to the amount of time it takes to recover data after a disruption, while RPO refers to the maximum tolerable data loss. By defining these objectives, businesses can ensure that their backup and restore processes align with their recovery goals.
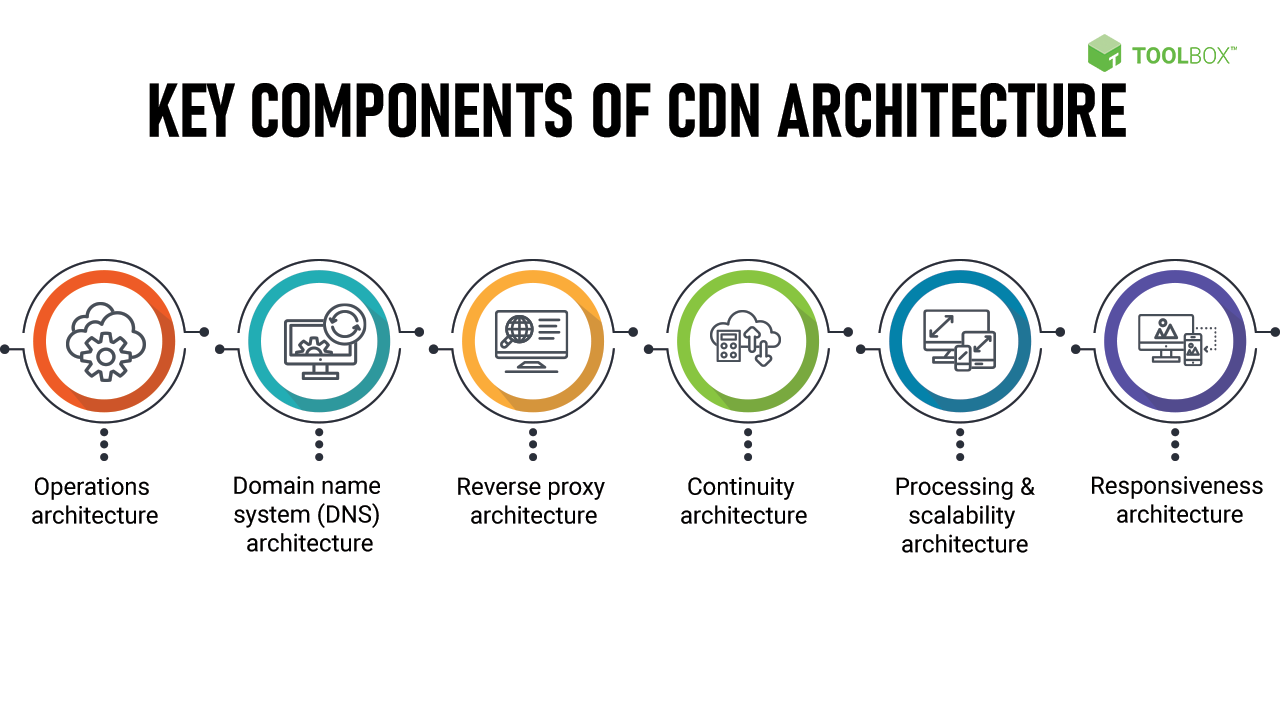
Components of a Cloud Backup and Restore Architecture
A comprehensive cloud backup and restore architecture comprises several key components that work together to ensure the seamless backup and recovery of data. Understanding these components is crucial for designing a robust architecture that meets your organization’s specific requirements.
Data Sources
The first component of a cloud backup and restore architecture is identifying the data sources that need to be backed up. This includes both structured and unstructured data generated by various applications, databases, and file systems. It is important to conduct a thorough inventory of data sources to ensure that all critical data is included in the backup process.
Backup Agents
Backup agents are software applications installed on servers, workstations, or other devices to facilitate the backup process. These agents are responsible for identifying and transferring data from the data sources to the cloud storage. They ensure that data is backed up efficiently and securely, taking into account factors such as data deduplication, compression, and encryption.
Cloud Storage
The cloud storage component is where the backed-up data is stored. Cloud storage providers offer various storage options, including object storage and block storage, each with its own advantages and use cases. When selecting a cloud storage provider, factors such as data durability, availability, and cost should be considered to ensure the reliability and accessibility of the stored data.
Recovery Mechanisms
The recovery mechanisms component encompasses the processes and tools used to restore data from the cloud backup. This includes features such as point-in-time recovery, granular file-level recovery, and disaster recovery options. Organizations should define their recovery requirements and select a cloud backup provider that offers the necessary recovery mechanisms to meet those requirements.
Data Transfer Methods
Data transfer methods play a crucial role in the efficiency and reliability of cloud backup and restore processes. Organizations can choose from various transfer methods, including direct connections, virtual private networks (VPNs), or secure file transfer protocols (SFTP). Selecting the appropriate data transfer method ensures the timely and secure transfer of data to the cloud storage.
Choosing the Right Cloud Backup Provider
With numerous cloud backup providers available in the market, selecting the right one for your organization can be a daunting task. However, considering certain factors can help you make an informed decision and choose a provider that aligns with your backup and restore requirements.
Reliability and Availability
When evaluating cloud backup providers, reliability and availability should be top considerations. The provider should have a proven track record of high uptime and minimal service disruptions. Additionally, they should have redundant systems and data centers to ensure data availability in the event of hardware failures or natural disasters.
Scalability and Flexibility
As your data grows, scalability becomes crucial. Ensure that the cloud backup provider offers scalable storage options that can accommodate your expanding backup needs. Additionally, flexibility in terms of storage plans and pricing models allows you to tailor the solution to your specific requirements and budget.
Security and Compliance
Data security is paramount when it comes to cloud backup. The provider should employ robust security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. They should also adhere to relevant compliance standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, depending on your industry and data privacy requirements.
Cost-effectiveness
While cost should not be the sole determining factor, it is important to consider the pricing structure and overall cost-effectiveness of the cloud backup provider. Compare pricing plans, storage costs, and any additional fees or hidden charges to ensure that the solution fits within your budget without compromising on quality and reliability.
Customer Support
Effective customer support is crucial when entrusting your data to a cloud backup provider. Evaluate the provider’s support options, response times, and availability. A responsive and knowledgeable support team can help address any issues or concerns promptly, ensuring minimal downtime and a smooth backup and restore experience.
Implementing a Cloud Backup Strategy
A well-defined cloud backup strategy is key to the success of your backup and restore architecture. It ensures that data is protected, recoverable, and aligned with your organization’s recovery goals. Here are the steps involved in developing a comprehensive cloud backup strategy.
Data Classification
Start by classifying your data based on its importance, sensitivity, and regulatory requirements. Categorize data into different tiers, such as critical, sensitive, and non-sensitive. This classification helps determine the backup frequency, retention policies, and security measures required for each data category.
Backup Frequency
Define how often data should be backed up based on its criticality and the frequency of changes. Critical and frequently changing data may require more frequent backups, while less critical data can be backed up less frequently. Striking the right balance between backup frequency and resource utilization is crucial.
Data Retention Policies
Establish data retention policies that align with your organization’s legal, compliance, and business requirements. Consider factors such as regulatory obligations, industry best practices, and the need for historical data for analysis or auditing purposes. Define retention periods for different data categories to ensure compliance and optimize storage costs.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Include disaster recovery planning as part of your cloud backup strategy. Identify potential disaster scenarios, such as hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks, and define recovery plans for each scenario. This may involve setting up redundant systems, performing regular backups, and testing the recovery processes to ensure their effectiveness.
Testing and Validating Backups
Regularly test and validate your backups to ensure their integrity and recoverability. Conduct periodic recovery tests to verify that backups can be successfully restored and that the recovered data is accurate and usable. Testing also helps identify any issues or gaps in the backup process that need to be addressed.
Automation and Monitoring
Automate the backup process as much as possible to minimize manual intervention and ensure consistency. Implement backup scheduling, monitoring, and alerting mechanisms to proactively identify any backup failures or anomalies. Regularly review backup logs and reports to ensure that backups are running smoothly and meeting the defined objectives.
Data Encryption and Security
Securing your data is of utmost importance when implementing a cloud backup and restore architecture. Data encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitivedata from unauthorized access. Here are some key considerations and methods for data encryption and security in your cloud backup and restore architecture.
Data Encryption Methods
There are various methods of data encryption that can be employed to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of your backed-up data. One common method is the use of encryption algorithms such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which is widely considered secure and efficient. AES encryption applies a mathematical algorithm to transform plaintext data into ciphertext, rendering it unreadable without the encryption key.
In addition to AES encryption, you can also consider other encryption techniques such as asymmetric encryption, which involves the use of public and private key pairs. With asymmetric encryption, data is encrypted with a recipient’s public key and can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key. This method is often used for secure data transmission and storage.
Encryption Key Management
Proper management of encryption keys is crucial for maintaining the security of your backed-up data. Encryption keys are used to encrypt and decrypt data, and their protection is essential to prevent unauthorized access. Consider using a secure key management system that securely generates, stores, and manages encryption keys.
Key rotation is another important aspect of encryption key management. Regularly rotating encryption keys helps mitigate the risk of compromised keys and enhances the overall security of your backup data. By changing encryption keys at defined intervals, you ensure that even if a key is compromised, it has a limited impact on the security of the entire dataset.
Access Controls and Authentication
Data access controls and authentication mechanisms play a critical role in ensuring that only authorized individuals can access your backed-up data. Implement strong access controls, such as role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC), to restrict data access to authorized personnel based on their roles, responsibilities, and permissions.
In addition to access controls, robust authentication mechanisms should be in place to verify the identities of individuals accessing the backup data. This can include multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device, to gain access to the data.
Data Integrity Verification
Data integrity verification ensures that the backed-up data remains unchanged and tamper-free throughout the backup and restore process. Implement mechanisms to regularly verify the integrity of your backup data, such as hash algorithms or checksums. These mechanisms generate unique values based on the data, allowing you to compare the calculated values with the original values to detect any modifications or corruption.
Regularly performing integrity checks on your backup data helps identify any potential issues or tampering, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the restored data. It is important to store the integrity verification values separately from the backup data to prevent tampering with both the data and the verification values.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Monitoring the performance of your cloud backup and restore architecture is crucial to ensure its effectiveness and optimize its operation. By monitoring key performance metrics and implementing performance optimization strategies, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your backup and restore processes.
Performance Metrics to Monitor
When monitoring your cloud backup and restore architecture, it is important to track and analyze various performance metrics. Some key metrics to consider include backup and restore speed, data transfer rates, backup success rate, and storage utilization. Monitoring these metrics allows you to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or potential issues and take appropriate measures to address them.
Additionally, monitoring the performance of your cloud backup provider is essential. Keep an eye on their service-level agreements (SLAs) and track metrics such as uptime, availability, and response times. If the provider fails to meet the agreed-upon performance levels, it may be necessary to consider alternative options to ensure the reliability of your backup and restore processes.
Optimizing Backup and Restore Performance
To optimize the performance of your backup and restore processes, consider implementing the following strategies:
Data Compression and Deduplication:
Utilize data compression and deduplication techniques to reduce the size of your backup data. Compression reduces the storage space required for backups, while deduplication identifies and eliminates redundant data, further optimizing storage utilization.
Bandwidth Management:
Manage your bandwidth effectively to ensure smooth data transfer between your organization’s systems and the cloud backup provider. Prioritize backup traffic and allocate sufficient bandwidth to prevent network congestion and minimize the impact on other critical business operations.
Backup Scheduling:
Optimize backup scheduling to minimize the impact on system resources and user productivity. Schedule backups during off-peak hours or during periods of low activity to ensure that backups do not interfere with normal business operations.
Incremental and Differential Backups:
Consider implementing incremental or differential backup strategies to minimize backup time and storage requirements. Instead of backing up the entire dataset each time, incremental backups only capture changes made since the last backup, while differential backups capture changes since the last full backup. These strategies reduce backup time and optimize storage utilization.
Parallelization:
If your cloud backup provider supports parallelization, consider utilizing this feature to improve backup and restore performance. Parallelization allows multiple backup or restore processes to occur simultaneously, reducing the overall time required for data transfer and recovery.
Cloud Backup and Restore Best Practices
Implementing best practices can help you maximize the effectiveness of your cloud backup and restore architecture. By following industry-proven strategies, you can ensure the reliability, security, and efficiency of your backup and restore processes. Here are some essential best practices to consider.
Regular Testing and Validation
Regularly test and validate your backup and restore processes to ensure their effectiveness and reliability. Perform periodic recovery tests to verify that backups can be successfully restored and that the recovered data is accurate and usable. Testing helps identify any issues or gaps in the backup process that need to be addressed.
Automation and Orchestration
Automate backup and restore processes as much as possible to minimize manual intervention and ensure consistency. Utilize backup management and orchestration tools to streamline the backup process, schedule backups, and automate error handling and reporting. Automation reduces the risk of human error and enhances the overall efficiency of your backup and restore architecture.
Data Retention and Archiving Policies
Establish clear data retention and archiving policies to ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Define retention periods based on industry best practices and your organization’s specific needs. Implement data archiving strategies for data that is no longer actively used but may still hold value for compliance or historical purposes.
Regular Audits and Reviews
Conduct regular audits and reviews of your backup and restore architecture to identify any potential security vulnerabilities, performance issues, or areas for improvement. Engage internal or external auditors to assess the effectiveness of your backup processes, adherence to security policies, and compliance with relevant regulations.
Education and Training
Invest in educating and training your employees on data backup and restore best practices. Ensure that they understand the importance of backup procedures, data security measures, and their individual responsibilities in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of backup data. Regularly update training materials to keep employees informed about the latest backup technologies and methodologies.
Continuous Improvement
Backup and restore technologies are constantly evolving, and it is important to stay up-to-date with the latest advancements. Continuously evaluate and assess emerging technologies, industry trends, and best practices to identify opportunities for improvement and optimize your backup and restore architecture.
Case Studies: Successful Cloud Backup Implementations
Real-life case studies provide valuable insights into how organizations have successfully implemented cloud backup and restore architectures. Let’s explore a few examples to understand the challenges faced, strategies employed, and the outcomes achieved.
Case Study 1: Company X – Ensuring Business Continuity
Company X, a global manufacturing firm, faced the challenge of protecting its critical data and ensuring business continuity in the event of a disaster. The company implemented a cloud backup and restore architecture, leveraging multiple redundant data centers to ensure data availability. Regular testing and validation of backups, along with automated recovery mechanisms, helped minimize downtime and facilitate quick restoration of services during disruptions.
The implementation of a cloud backup solution allowed Company X to scale its backup infrastructure as its data volumes increased, eliminating the need for costly hardware investments. The company also implemented encryption and access controls to ensure the security of its backed-up data, complying with industry regulations and customer demands.
Case Study 2: Organization Y – Streamlining Backup Operations
Organization Y, a healthcare provider, struggled with managing the backup and restore of its sensitive patient data across multiple locations. By adopting a cloud backup and restore architecture, the organization centralized its backup operations, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
The implementation involved integrating backup agents with the organization’s existing systems and applications, ensuring seamless data capture and transfer to the cloud. Incremental backups and data deduplication techniques were employed to optimize storage utilization and reduce backup time. Regular audits and reviews were conducted to ensure compliance with healthcare regulations and maintain the security and privacy of patient data.
Future Trends in Cloud Backup and Restore
The field of cloud backup and restore architecture is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Here are some emerging trends that are shaping the future of cloud backup and restore.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine LearningArtificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing the backup and restore landscape. These technologies enable intelligent data management, automation, and predictive analytics. AI-powered algorithms can analyze data patterns, identify anomalies, and optimize backup strategies based on usage patterns, data types, and criticality. ML algorithms can also help improve data deduplication and compression techniques, reducing storage requirements and enhancing overall backup efficiency.
Blockchain for Data Integrity
Blockchain technology is being explored for enhancing data integrity in cloud backup and restore architectures. By utilizing the decentralized and distributed nature of blockchain, organizations can ensure the immutability and verifiability of their backed-up data. Blockchain-based backups provide an additional layer of security and transparency, making it harder for malicious actors to tamper with or manipulate the backup data.
Edge Computing and Backup
With the rise of edge computing, where data processing and storage occur closer to the data source, backup and restore architectures are adapting to this new paradigm. Edge computing allows for faster backup and recovery times, as data does not need to be transferred over long distances to the cloud. Organizations are exploring hybrid backup approaches, combining local edge backups with cloud-based offsite backups, to achieve both speed and data redundancy.
Ransomware Protection and Recovery
Ransomware attacks continue to pose a significant threat to organizations, making ransomware protection and recovery an important focus in cloud backup and restore architectures. Backup solutions are being enhanced with built-in ransomware detection and mitigation capabilities. These features help identify and isolate infected files, enabling rapid recovery of clean data without paying the ransom demand.
Compliance and Data Privacy
As data privacy regulations become more stringent, cloud backup and restore architectures are evolving to ensure compliance. Backup providers are implementing features such as data residency options, encryption, and audit trails to meet the requirements of regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Organizations are also adopting privacy-enhancing technologies like differential privacy to protect individual data while still enabling effective backup and restore processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does it take to restore data from a cloud backup?
A: The time taken to restore data from a cloud backup depends on various factors such as the volume of data, the speed of the internet connection, and the recovery mechanisms employed. While smaller amounts of data can be restored relatively quickly, larger datasets may take longer. It is essential to consider the recovery time objective (RTO) when designing your backup and restore strategy.
Q: Is cloud backup secure?
A: Cloud backup can be secure if proper security measures are implemented. It is crucial to choose a reputable cloud backup provider that offers data encryption, access controls, and other security features. Additionally, organizations should implement strong authentication and encryption key management practices to enhance the security of their backed-up data.
Q: Can I backup and restore specific files from a cloud backup?
A: Yes, most cloud backup solutions allow for granular file-level recovery. This means you can select and restore specific files or folders from your backup instead of restoring the entire dataset. Granular recovery provides flexibility and efficiency, allowing you to retrieve only the necessary files without the need for a full restore.
Q: Can I backup multiple devices to the same cloud backup account?
A: Yes, many cloud backup providers offer multi-device backup capabilities. You can back up multiple devices, such as computers, servers, and mobile devices, to the same cloud backup account. This allows for centralized management and ensures that all critical devices are protected with regular backups.
Q: How often should I test my cloud backups?
A: It is recommended to regularly test your cloud backups to ensure their reliability and recoverability. The frequency of testing depends on the criticality of your data and the rate of changes in your systems. Conducting periodic recovery tests, at least once every few months, helps identify any issues or gaps in your backup process and allows you to address them before an actual data loss event occurs.
Q: Can I use cloud backup for disaster recovery?
A: Yes, cloud backup can be an integral part of your disaster recovery strategy. By storing your backup data in the cloud, you can quickly recover your critical systems and data in the event of a disaster. Cloud backup allows for offsite storage, redundancy, and scalability, making it an ideal solution for disaster recovery scenarios.
Q: What happens if my internet connection goes down during a backup or restore process?
A: If your internet connection goes down during a backup or restore process, the process will pause until the connection is restored. Modern cloud backup solutions often have mechanisms to resume interrupted backups or restores once the internet connection is available again. It is important to ensure a stable and reliable internet connection to minimize disruptions in the backup and restore processes.
Q: Can I access my cloud backups from anywhere?
A: Yes, one of the advantages of cloud backup is the ability to access your backed-up data from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud backup providers typically offer web-based interfaces or dedicated applications that allow authorized users to access and restore their data remotely. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for businesses with remote workers or those requiring access to critical data during off-site operations.
Q: Can I encrypt my backed-up data using my own encryption algorithms?
A: Some cloud backup solutions provide the option to use customer-managed encryption keys or allow for the use of custom encryption algorithms. This gives you control over the encryption process and allows you to use your preferred encryption methods. However, it is important to ensure that your chosen encryption algorithms are secure and comply with industry standards.
Q: Can I integrate cloud backup with my existing backup infrastructure?
A: Yes, many cloud backup providers offer integration options to seamlessly integrate with existing backup infrastructure. This allows businesses to leverage their investments in on-premises backup solutions while taking advantage of the scalability and flexibility of cloud storage. Integration capabilities may include APIs, software agents, or gateway devices that enable the transfer of backup data to the cloud.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a robust and well-designed cloud backup and restore architecture is crucial for protecting and recovering your valuable data. By understanding the key components, best practices, and emerging trends, you can optimize your backup and restore operations and ensure business continuity. Remember to choose a reliable cloud backup provider, implement strong security measures, and regularly evaluate and update your backup strategy to stay ahead in this ever-evolving digital landscape.
We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable insights into cloud backup and restore architecture. If you have any further questions or require assistance, feel free to reach out to our team of experts. Happy backing up!